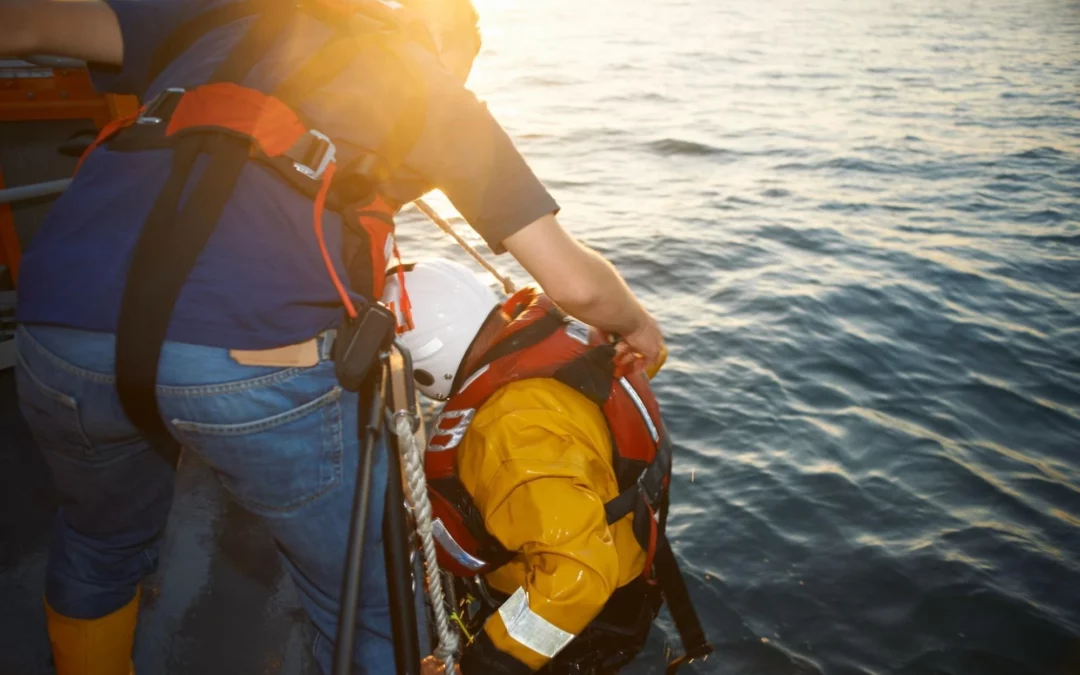
by Barani Chettiar | Mar 9, 2024 | Uncategorized
Importance of MOB Systems in Maritime Safety
Navigating the unpredictable waters of commercial maritime operations demands an unwavering commitment to safety. Man Overboard (MOB) incidents pose a significant threat, requiring proactive measures to enhance response times and minimize risks. This blog post delves into the critical role of MOB systems in safeguarding lives and ensuring the well-being of crew members in the challenging maritime environment.
Understanding Man Overboard Incidents
Frequency and Severity
Man Overboard incidents are unfortunately not uncommon in the maritime industry. Factors such as adverse weather conditions, vessel motion, and human error contribute to the occurrence of MOB situations, emphasizing the need for effective prevention and response mechanisms.
Challenges in Detection
Locating a person who has fallen overboard swiftly is a race against time. The vastness of the sea, limited visibility, and rapid drift make manual detection challenging, necessitating the integration of advanced MOB systems.
Types of Man Overboard Systems
Electronic MOB Alarms
Electronic MOB alarms utilize sensors, GPS technology, and alarms to detect and alert the crew when someone falls overboard. These systems provide real-time information, enabling quick response and increasing the chances of a successful rescue.
AIS MOB Beacons
AIS (Automatic Identification System) MOB beacons are compact devices that transmit MOB alerts and position information to nearby vessels equipped with AIS receivers. This technology enhances coordination between vessels during rescue operations.
Benefits of Implementing MOB Systems
Rapid Response
MOB systems significantly reduce the time it takes to detect and respond to a person falling overboard. Swift response improves the chances of successful retrieval and minimizes the potential impact on the individual’s health and safety.
Crew Confidence and Morale
Knowing that advanced MOB systems are in place boosts the confidence and morale of crew members. The assurance that their safety is a priority contributes to a positive working environment.
Regulations and Standards for MOB Systems
HOLAS Requirements
The International Maritime Organization’s Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) regulations outline requirements for MOB systems on certain vessels. Compliance with SOLAS standards ensures a baseline level of safety for vessels navigating international waters.
Flag State Regulations
Individual flag states may have additional or specific regulations regarding MOB systems. It is essential for vessel operators to be aware of and adhere to the regulations applicable to their flag state.
Training and Education for Crew Members
MOB Drills
Regular MOB drills are essential to familiarize the crew with the operation of MOB systems and refine their response protocols. Practical training ensures a coordinated and effective response in the event of an actual MOB incident.
Crew Awareness
Educating the crew about the importance of MOB systems, their functionalities, and the role each crew member plays in MOB response is crucial. Awareness contributes to a culture of safety on board.
Ensuring Safety Through MOB Systems
In conclusion, the implementation of Man Overboard (MOB) systems is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a fundamental commitment to the safety and well-being of crew members at sea. Whether you are in search of marine navigation equipment or exploring MOB systems, www.tecomart.co offers a range of solutions to meet the unique needs of your vessel. By embracing advanced MOB technology, commercial maritime operators can navigate with confidence, knowing that they are equipped to respond swiftly and effectively to MOB incidents, safeguarding lives and ensuring a secure maritime environment.

by Barani Chettiar | Mar 8, 2024 | Uncategorized
Importance of Marine Radio Communications
In the expansive world of commercial maritime operations, effective communication is the linchpin for safety and operational efficiency. Marine radio systems stand as the backbone, connecting vessels, ensuring coordination, and providing a lifeline in emergencies. This guide unravels the complexities of marine radio frequencies and channels, offering invaluable insights for commercial operators navigating the seas.
Understanding Radio Frequencies: VHF, UHF, HF Differences
Very High Frequency (VHF)
VHF marine radios, operating between 156 and 174 MHz, excel in short-range communication. Perfect for ship-to-ship and ship-to-shore interactions, VHF frequencies provide clear and reliable communication within line-of-sight distances.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
UHF marine radios, spanning 400 to 512 MHz, offer a shorter wavelength, making them ideal for confined spaces or areas with obstacles. While their range is limited compared to VHF, UHF frequencies are valuable in specific maritime scenarios.
High Frequency (HF)
Covering a broader range from 3 to 30 MHz, HF marine radios are known for long-range communication capabilities. Despite their extensive reach, HF radios are less prevalent in commercial use due to the prevalence of VHF and UHF systems.
Marine Radio Channels: Purpose and Usage Explained
Navigating the ocean of radio channels requires a comprehensive understanding of their purpose and usage.
VHF Channel 16 – International Hailing and Distress
Known as the universal calling channel, VHF Channel 16 is dedicated to distress calls and international hailing. Essential for emergencies, it ensures a standardized platform for seeking assistance.
VHF Channel 9 – Boater Calling
Designated for non-commercial vessels, Channel 9 is a key frequency for boater calling, facilitating general communication and coordination among recreational and small-scale maritime users.
VHF Channel 13 – Bridge-to-Bridge
Primarily used for communication between vessels approaching bridges, locks, and narrow channels, Channel 13 aids in coordinating safe passage and avoiding collisions.
Commercial Use Regulations: Licensing Requirements and Restrictions
Licensing Requirements
In Singapore and many maritime jurisdictions, commercial operators must obtain the necessary licenses to operate marine radios legally. Compliance ensures that operators are trained and aware of proper radio usage.
Frequency and Channel Restrictions
Regulations impose restrictions on specific frequencies and channels to prevent interference. Familiarize yourself with these restrictions to maintain clear communication and avoid unintended violations.
Emergency Procedures: Distress Calls and Safety Protocols
Distress Calls
In emergencies, clear communication is paramount. Familiarize yourself with the proper distress call protocols, including the use of Digital Selective Calling (DSC), to swiftly and effectively communicate distress situations.
Safety Protocols
Understanding safety protocols, such as the “Mayday” and “Pan-Pan” calls, enhances emergency communication. Proper execution ensures that distress situations are communicated effectively, enabling a swift response from nearby vessels or rescue services.
Communication Best Practices: Etiquette and Effective Communication Tips
Etiquette
Maintaining communication etiquette is crucial for efficient and courteous interactions. Adhere to established procedures, avoid unnecessary transmissions, and use appropriate channels to foster a harmonious radio environment.
Effective Communication Tips
Enhance communication effectiveness with clear and concise language, especially in critical situations. Regular radio checks and monitoring designated working channels promote efficient communication among vessels in close proximity.
Key Takeaways for Commercial Marine Operators
As commercial marine operators sail into the future, equipped with handheld VHF marine radios and advanced communication technology, understanding marine radio frequencies and channels is non-negotiable. Whether you are exploring handheld radios for sale or seeking digital mobile radio solutions, www.tecomart.co provides a range of equipment to meet your communication needs. Arm yourself with knowledge, adhere to regulations, and embrace best practices to navigate the seas with confidence and precision.
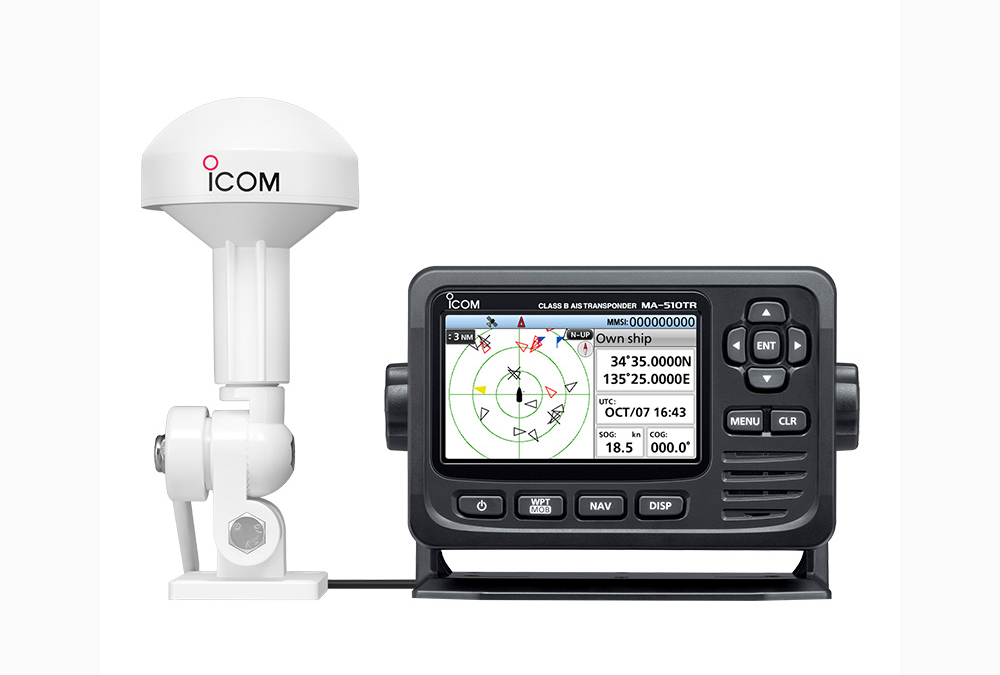

by Barani Chettiar | Mar 7, 2024 | Uncategorized
In the vast expanse of our oceans, where commerce sails on mighty vessels, ensuring safety and efficient navigation becomes paramount. Automatic Identification System (AIS) has emerged as a technological beacon, illuminating the maritime landscape with its capabilities. This blog post dives into the depths of AIS, shedding light on its significance for commercial vessels and the intricate web it weaves in the vast sea.
What is AIS?
Automatic Identification System, or AIS, is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the maritime industry. Simply put, AIS is a tracking system used on ships for the exchange of data within a particular range. This system facilitates real-time communication between vessels, shore stations, and even other navigational aids, ensuring a seamless flow of critical information.
The AIS technology is classified into two main types: Class A AIS transponder and Class B AIS transponder. The former is typically mandatory for larger vessels and provides a more comprehensive set of data, including identity, position, course, and speed. On the other hand, the Class B AIS transponder, while not mandatory, is commonly used by smaller vessels and provides essential information for collision avoidance.
Benefits of AIS
AIS brings a multitude of benefits to the maritime domain, enhancing both safety and navigation. One of its primary advantages is the improved visibility it offers to vessels in close proximity. The exchange of real-time information allows for early detection of potential collisions, reducing the risk of accidents at sea. Additionally, AIS aids in the identification of vessels, streamlining communication and coordination between ships. This proves particularly valuable in congested waterways and busy ports, where the swift exchange of information is crucial for maintaining order and safety.
In Singapore, a bustling maritime hub, the adoption of AIS has significantly contributed to the overall efficiency of port operations. The implementation of AIS technology aligns with the city-state’s commitment to maritime safety and its role as a global shipping hub.
Transmitting and receiving vessel data
AIS operates on the principle of VHF (Very High-Frequency) transmissions, utilizing VHF marine radio frequencies for communication. Vessels equipped with AIS transponders continuously broadcast their identification, position, course, and speed information. Simultaneously, they receive and process similar data from other vessels within range. This dynamic exchange of information creates a comprehensive maritime picture, enabling vessels to navigate through busy waterways with heightened situational awareness. The seamless integration of AIS into navigational practices has become a cornerstone of modern maritime safety protocols.
International maritime requirements for AIS
Recognizing the pivotal role AIS plays in maritime safety, international regulations mandate its use in certain vessels. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has set forth guidelines for the installation and operation of AIS, emphasizing its implementation in larger vessels and those navigating in high-traffic areas. For Singaporean vessels, adherence to these international standards ensures seamless interoperability with vessels worldwide, contributing to the nation’s commitment to safe and efficient maritime operations.
Challenges and drawbacks of AIS technology
While AIS has proven to be a game-changer in maritime safety, it is not without its limitations. One of the challenges lies in the vulnerability of the system to cyber threats. Unauthorized access to AIS data poses potential risks, necessitating continuous advancements in cybersecurity measures to safeguard maritime communication. Moreover, the reliance on VHF frequencies for AIS communication limits its effectiveness in certain situations, such as over-the-horizon tracking. Despite these challenges, ongoing developments in technology aim to address these limitations and fortify the resilience of AIS in the face of evolving threats.
Importance of AIS in commercial shipping
In the intricate dance of vessels on the high seas, Automatic Identification System emerges as a guiding force, fostering safety, efficiency, and international cooperation. From the mandatory Class A AIS transponder to the bustling ports of Singapore, AIS technology weaves a seamless tapestry of communication, ensuring that ships navigate the waters with precision and caution. As technology evolves, so does the role of AIS in shaping the future of commercial shipping. The continuous refinement of AIS, coupled with stringent international regulations, paves the way for a maritime landscape where safety is paramount, and vessels sail confidently into a future propelled by innovation and collaboration.
by Barani Chettiar | Jan 30, 2024 | Uncategorized
Navigating the vast and often unpredictable expanse of the open seas requires mariners to rely on a standardised system of markers. The International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA) Buoyage System is a crucial component of marine navigation, providing a uniform set of sea marks globally. To help you further understand its importance, we give you insight into its scope and the various types of marks you should note.
What Is the IALA Buoyage System?
The IALA Buoyage System is the backbone of international marine navigation, establishing a standardised set of sea marks to safely guide vessels through waterways. These uniform navigational aids also help protect the marine environment, preventing vessels from crossing vulnerable areas.
Adopted by most maritime nations, the system is divided into two regions: Region A and Region B. Region A encompasses Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Africa and Asia, while Region B covers North, Central, and South America, Japan, and the Philippines.
Differentiating Aids to Sea Navigation: Buoys and Beacons
Central to the IALA Buoyage System are aids to sea navigation and crucial markers that guide mariners through channels and indicate potential hazards. Two primary types of aids are buoys and beacons.
Buoys
Buoys are floating markers which are anchored to the seabed. They have distinctive shapes and colours to indicate their purpose and how to navigate around them. Buoys are mobile and strategically positioned to mark channels and hazards and provide directional information.
Beacons
On the other hand, beacons are fixed structures mounted on solid ground and often onshore or atop structures like lighthouses. The majority of beacons have lateral or non-lateral aids attached to them. For example, light beacons are called “LIGHTS,” while those without lights are called “DAYBEACONS.”
Types of Marks in the IALA Buoyage System
As you navigate through the sea, here are the types of marks under the IALA Buoyage System:
Lateral Marks

These marks guide vessels on which side of the waterway to follow. Lateral marks can be port or starboard lateral marks, denoted by their colours. For example, in Region A, the colour of the port hand mark, which is found on the left, is red, while the starboard mark, found on the right, is green. For waters in Region B, the colours are reversed, with the port side mark on the left in green and the starboard mark on the right in green.
Cardinal Marks
Cardinal marks derive their name from the cardinal points of the compass: north, east, south, and west. They are crucial navigational aids that help mariners identify the deepest water in a specific area and indicate the safe side to navigate potential hazards. Moreover, they draw attention to notable features within a channel, such as bends, junctions, or the termination of a shoal.
Notably, Region A and Region B adhere to a consistent colour scheme for their cardinal marks, employing black and yellow markings and distinctive top marks.
Isolated Danger Marks
These signify a hazard to shipping, like a wreck or submerged rock. Isolated danger marks typically stand or are moored above the hazard. One of the distinct characteristics of this mark is its double sphere top mark, which needs to be visible during the day. Moreover, the isolated danger mark should be as large as possible, with spheres clearly separated.
Safe Marks
When encountering a safe water mark, this means that there is navigable water all around the mark, which includes the end of a channel or mid-channel. It is typically in red and white vertical stripes and has a single red sphere as a top mark.
Special Marks
Special marks are used to indicate areas where specific regulations apply, such as mooring areas, recreational zones, or underwater pipelines. These marks are yellow in colour with a single yellow “X” shape as the top mark.
Find High-Quality Marine Navigation Equipment at Tecomart
As you navigate vast waters across regions of the world guided by the IALA Buoyage System, having reliable marine navigation equipment on your vessel is also important. When seeking essential navigational devices for your voyage at sea, you should turn to a trusted supplier offering a diverse array of equipment from reputable manufacturers like Garmin, JRC, and Furuno. This is where Tecomart excels. Explore our extensive catalogue of marine navigation equipment, and choose from our selection of quality GPS chart plotters, marine video cameras, and marine radars for sale. At Tecomart, we prioritise high-quality marine navigation equipment to enhance your safety at sea.
If you want more marine navigation tips, you can check out our tips for taking over navigational watches and safe sailing at night.

by Barani Chettiar | Jan 29, 2024 | Uncategorized
Despite mobile phones becoming the most common means of communication, handheld radios remain indispensable in various applications, from emergency response to recreational outdoor activities. They provide a dedicated and efficient channel of communication that can operate independently of cellular networks, which is especially important when signals for mobile networks become weak or fail. Moreover, handheld radios offer a secure and instantaneous mode of communication, which allows teams to coordinate seamlessly even in challenging environments.
If you’re planning to get your own handheld radio, whether for business or recreational use, we give you insight into the different types of handheld radios and what to consider when buying one.
Different Types of Handheld Radios
There are two basic types of handheld radios. Understanding the features and benefits of each type allows you to make an informed decision on what would be best suited for your needs.
Analogue Handheld Radios
Analogue radios, also known as two-way handheld radios, have been the traditional choice for communication. They use analogue signals to transmit voice communication and are known for their simplicity and ease of use. Analogue radios are suitable for basic communication needs and are often less expensive than their digital counterparts.
Digital Handheld Radios
On the other hand, digital handheld radios are frequently employed by businesses seeking to optimise real-time communication across various devices. They offer features such as background noise cancellation and extended coverage capabilities to ensure teams have clear and efficient communication.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Handheld Radio
Here is what you should consider when selecting the right handheld radio for your needs:
Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
Handheld radios transmit signals over a radio channel using either a Very High Frequency (VHF) or Ultra High Frequency (UHF) carrier frequency wave. Each frequency range has its distinct advantages and considerations.

Radios operating on Very High Frequency or VHF typically offer better performance in open spaces with minimal obstructions. The longer wavelengths of VHF signals make them more effective in covering larger distances. This makes VHF handheld radios well-suited for outdoor activities, such as hiking or open-field events where line-of-sight communication is vital.
On the other hand, handheld radios with Ultra High Frequency or UHF excels in areas with numerous obstructions, such as buildings or dense forests. The shorter wavelengths of UHF signals can penetrate obstacles more effectively, making them suitable for indoor use, urban environments, and scenarios where communication may encounter physical barriers.
These days, there are handheld radios available which can transmit signals to both VHF and UHF frequencies. One example would be the ICOM IC-T10 DUAL BAND FM TRANSCEIVER, which is great for long-range communication. With a powerful 5W RF output in both the 144 and 430 MHz bands, it ensures your signal reaches far and wide.
To know which frequency your type of application requires, check out our guide on choosing between UHF and VHF handheld radios.
Range Capabilities and Requirements
The range of a handheld radio is a critical factor to consider, especially if you anticipate communication over long distances. Radios with higher power output and longer antennas generally offer greater range. However, it’s essential to balance range requirements with power consumption, as higher power settings can drain the battery more quickly. Assess your communication needs and select a handheld radio that provides sufficient range without compromising battery life.
Durability and Resistance to Environmental Factors

Handheld radios are often used in challenging environments, ranging from bustling warehouses to critical emergency situations. Therefore, prioritising durability and resistance to environmental factors becomes paramount. When evaluating a handheld radio’s durability, consider the construction quality and the materials used.
If you want a handheld radio that stands up to the rigours of outdoor use, the Yaesu VX-110 Transceiver proves to be an exemplary choice. With a robust die-cast aluminium housing, this two-way radio ensures unparalleled durability, making it an ideal communication device for demanding environments.
Size and Weight

The size and weight of a handheld radio can significantly impact its usability, especially if you plan to carry it for extended periods. Compact and lightweight radios are ideal for outdoor activities and events, ensuring they won’t become a burden during extended use.
For a reliable and lightweight handheld radio, you can consider options such as the FT-10R VHF Transceiver. This model, in particular, combines a compact design with user-friendly features, making it an excellent choice for users prioritising portability without compromising functionality.
For High-Quality Handheld Radios, Choose Tecomart
Should you need top-notch amateur radio equipment, look no further than Tecomart. Renowned for delivering excellence in radio communication, Tecomart offers a comprehensive range of high-quality equipment tailored for various applications. Whether you are in search of feature-rich handheld radio sets, reliable two-way radio repeaters, or other communication solutions, our extensive catalogue has you covered. At Tecomart, we prioritise performance, durability, and innovation, ensuring that the products we supply can meet your recreational and business needs. Explore our offerings today.
For further insight into radio communication equipment, see what mistakes you should avoid with your amateur radio equipment.